EDI is like the postal service—standardized, reliable, and built for bulk. APIs are like instant messaging—flexible, immediate, and made for real-time interaction.
Enterprises still need the ‘postal service’ to move large, critical volumes across global networks where consistency is non-negotiable. But they also need the ‘instant messages’ to enable real-time visibility and agility in fast-changing supply chain environments.
This is the heart of the debate: API vs EDI in supply chain. Will APIs replace EDI? Or can both coexist to power the next generation of digital supply chain solutions?
In this blog, we’ll explore the differences, strengths, coexistence models, and the future outlook for EDI and APIs—so leaders can make informed integration decisions.
What is EDI and Why Has It Been Foundational?
Electronic Data Interchange has been the trusted language spoken between global trade partners for decades. EDI has been the go-to option, especially for companies with strict compliance needs, enabling the secure, structured, and error-free electronic exchange of high-volume critical business documents.
Even today, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in supply chain remains essential. But as the workforce shifts, many question whether “legacy” EDI will eventually give way to APIs, especially given EDI’s perceived limitations:
- EDI is often batch-oriented, meaning updates are delayed. Example: A retailer using EDI may only receive daily inventory updates from suppliers, so if a product sells out in the morning, the system may not reflect the shortage until the next batch update, causing stockouts or overselling.
- People say that due to outdated software, custom code, and tightly coupled workflows, EDI modernization might require significant investment in consulting, testing, and employee training.
- Lack of agility compared to newer integration methods. For example, legacy EDI may not support instant updates such as real-time shipment tracking and automated alerts, whereas APIs could push notifications immediately, allowing faster responses to delays or exceptions.
So, legacy EDI systems vs modern APIs has become an unavoidable comparison.
What is API and Its Role in Modern Supply Chains?
In comparison, Application Programming Interface (API) provides on-demand connectivity – no more batch processing delays, so to speak. In a supply chain context, API aligns better with instant data exchange across CRMs, ERPs, and cloud-native analytical tools, quicker than setting up a full EDI. You get real-time shipment tracking, dynamic routing, and last-mile delivery updates on the go.
API too has its own set of challenges:
- Scalability can be an issue for very large, high-volume data exchanges where EDI still excels.
Example: A global retailer trying to process thousands of purchase orders per hour via APIs may experience slowdowns or timeouts, whereas their legacy EDI system, built for batch processing, handles the same volume reliably.
- Requires ongoing governance to manage multiple APIs securely.
Example: A logistics company integrates APIs from multiple shipping partners for real-time tracking. Each API has different authentication methods, rate limits, and data formats. Without continuous monitoring, version updates or security breaches could disrupt operations or expose sensitive data. In contrast, EDI uses standardized formats and established protocols, making it more predictable and easier to manage across multiple partners.
And thus, APIs are not about replacing EDI, they’re about expanding the possibilities of modern supply chain technology, working hand-in-hand with EDI.
API vs EDI: A Comparative View
| Feature | EDI | API |
| Format | Structured, standardized (X12, EDIFACT) | Flexible, JSON/XML-based |
| Processing | Batch-oriented | Real-time |
| Use Case | High-volume, compliance-driven transactions | Real-time tracking, analytics, agile workflows |
| Security | Proven standards, trusted for decades | Modern authentication (OAuth, tokens) |
| Integration Speed | Slower, costly to modernize | Faster, agile |
This API and EDI comparison highlights a key truth: both solve different problems.
Can APIs Replace EDI? (The Misconception)
Many think APIs are here to retire EDI, but that’s like assuming WhatsApp will make email vanish overnight. While APIs bring real-time speed and agility, EDI remains the trusted workhorse for high-volume, compliance-driven transactions.
EDI modernization is alive and kicking because:
- Retail giants still mandate EDI compliance for suppliers.
- Healthcare requires EDI transactions for regulatory reasons.
- Automotive OEMs rely on established EDI workflows for just-in-time manufacturing.
So, when executives ask: EDI vs API—which is better? The answer is—it depends. In truth, they serve different purposes, neither replaces the other; they complement each other, combining reliability with responsiveness to power a truly modern, hybrid digital supply chain. Both are necessary.
Why APIs and EDI Must Coexist in a Digital Supply Chain
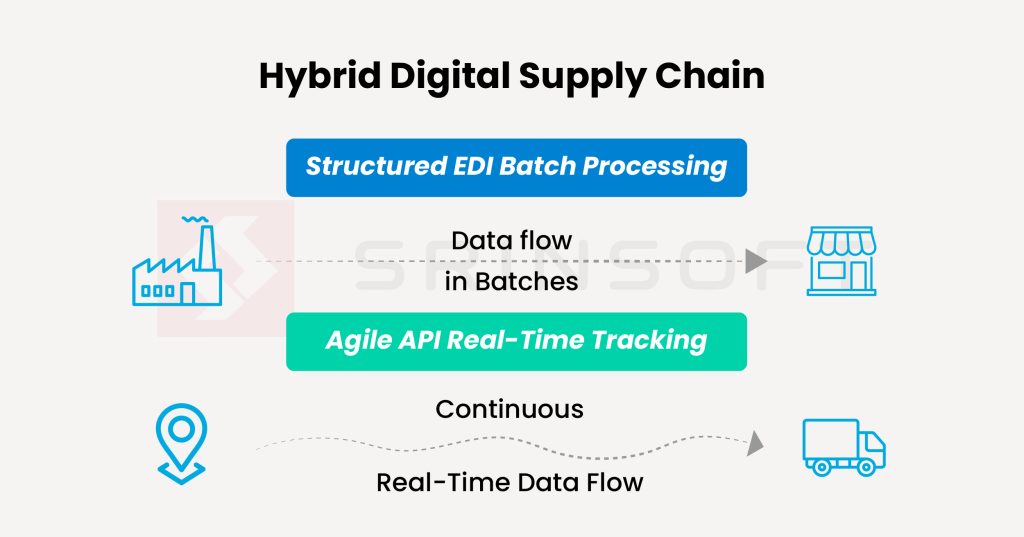
For supply chain enterprises, the real opportunity lies in API and EDI coexistence, the reliability of EDI and the responsiveness of APIs. Think of it as layering agility on top of reliability, like adding Wi-Fi on a trusted wired network.
Scenarios of coexistence:
Here are some realistic supply chain scenarios that show how EDI and APIs actually complement each other:
- Inventory status reports (EDI 846):
A retailer sends bulk stock availability data to suppliers via EDI once a day. An API layer adds real-time warehouse feeds, so if a hot-selling item drops below threshold, suppliers are alerted instantly. - Forecasts and planning schedules (EDI 830):
An auto manufacturer shares quarterly demand forecasts with parts suppliers over EDI. Meanwhile, APIs pull live sales data from dealerships, helping suppliers adjust production schedules faster when demand spikes unexpectedly. - Payment remittance advice (EDI 820):
A distributor sends EDI 820 to confirm a bulk payment covering hundreds of invoices. APIs let the supplier check payment clearance status in their bank system immediately instead of waiting for the next reconciliation cycle. - Customs documentation (EDI 309/310):
An international freight carrier transmits customs manifest data to authorities over EDI for compliance. APIs from logistics providers let shippers track the same container’s real-time GPS location and customs clearance status. - Product catalogs (EDI 832):
A consumer electronics brand distributes seasonal products and pricing data to retailers through EDI. APIs then allow online marketplaces to pull live pricing updates or flag when a product goes out of stock.
EDI vs API integration: How to Integrate API and EDI in Supply Chain Successfully
For enterprises, the path forward is a hybrid integration strategy:
- Hybrid Integration Platforms (iPaaS): Using an IPaaS solution that connects your EDI with cloud-based APIs, you can see both bulk B2B orders and real-time online sales in one system.
- Unified Dashboards: With a single dashboard that displays nightly EDI shipment manifests alongside API-driven live GPS tracking data, managers no longer need to switch between systems to see both batch and real-time movements.
- Automation-first mindset: You can set up an API trigger so that when a customer places a large order online, it automatically generates an EDI 830 (planning schedule) for the supplier. Conversely, when the supplier sends an EDI 846 (inventory status), an API immediately updates your website to show current stock levels.
Future of Digital Supply Chain: Unified API + EDI Ecosystems
Looking ahead, supply chains won’t be “EDI-only” or “API-only.” Instead, they’ll be cloud-first ecosystems where both technologies coexist:
- EDI for compliance and high-volume exchanges.
- APIs for agility, analytics, and customer experience.
- AI/ML-enabled integration platforms will add predictive insights, anomaly detection, and automated exception handling.
It’s the evolution of supply chains—APIs driving innovation at the surface, while EDI continues to provide the solid foundation required for global compliance and high-volume exchanges.
Quantifiable Benefits of Hybrid Edi + API Integration
Conclusion
So, API vs EDI: Can They Coexist in a Digital Supply Chain? The answer is a definite yes!
In fact, the debate around API vs EDI in the digital supply chain misses the point; these aren’t competitors.
The future of supply chain isn’t about choosing between the postal service and instant messaging; it’s about having both in your communication arsenal. Smart enterprises are building hybrid ecosystems where EDI continues handling the heavy lifting of global compliance and bulk transactions, while APIs add the real-time agility that modern customers demand.
The question isn’t whether APIs will replace EDI; it’s whether you’ll integrate both before your competition gains an insurmountable advantage in customer experience and operational efficiency.
The Cost of Inaction – Why This Matters to Your Bottom Line
1. Trading Partner Abandonment Risk
Major retailers like Walmart and Amazon are mandating API capabilities alongside EDI compliance; companies that can’t deliver both face losing accounts.
2. Competitive Displacement Risk
Competitors with hybrid integration can onboard new suppliers 5x faster and respond to market changes in hours vs. days, systematically capturing market share while you’re stuck in batch-processing delays.
3. Operational Blind Spot Risk
Without real-time API visibility layered on EDI transactions, supply chain disruptions go undetected for 12-48 hours, turning problems into crisis events.
4. Technical Debt Explosion Risk
Delaying integration forces expensive custom workarounds and manual processes that compound yearly.
5. Regulatory Compliance Failure Risk
Industries like healthcare and automotive are adding real-time reporting requirements to existing EDI mandates; companies without hybrid capabilities face fines and potential loss of operating licenses.
Transform Your Supply Chain with SrinSoft Technologies
At SrinSoft, we specialize in harmonizing legacy EDI systems with modern API architectures, creating a robust, agile, and future-ready digital supply chain.
Our EDI Services Include:
- Tailored EDI Development
- Trading Partner Onboarding
- Mapping & Automation
- Comprehensive EDI Testing
- Software Upgrades & Configuration
- Back-Office Integration
Our API Integration Expertise:
- Platform and API Services Integration
- Middleware Solutions
- Custom Application Integrations
- Digital Transformation Enablement
Ready to optimize your supply chain? Contact us today for a free integration audit!
FAQs
1. Will APIs replace EDI?
No. It’s more like EDI evolving—shedding its old skin and stepping out as a brighter, more agile, API-enhanced version. Industries like healthcare, retail, and automotive rely on EDI compliance.
2. EDI vs API which is better?
Neither is universally better. EDI, like your dominant arm, handles the heavy lifting of bulk transactions, while APIs act as the other hand, bringing agility and speed with real-time updates. And together, they form a complete grip—giving enterprises both strength and precision in their supply chain integrations.
3. Can EDI and APIs work together in logistics?
Yes, absolutely. EDI–API coexistence works to your advantage. The combination brings balance: EDI manages bulk invoices reliably, while APIs deliver real-time shipment tracking for complete visibility.
4. What’s the future of supply chain integration?
Imagine a conjoined jellyfish—flexing, adapting, and moving as one, each part filling in where the other is needed. That’s a hybrid model combining legacy EDI systems with modern APIs: a unified, cloud-first ecosystem that blends the reliability of EDI with the real-time agility of APIs.